How the China Trade Deal Affects the U.S. Economy
The U.S.–China trade relationship is one of the most important bilateral economic engagements in the world. In 2025, both nations agreed on a pivotal trade deal that has begun reshaping the global economic landscape. After years of tariff hikes, economic disputes, and political tensions, the newly signed china trade deal marks a step toward stability, with significant effects on the U.S. economy. This blog explores the details of the agreement and its broader economic, political, and social consequences for the United States.
What Is the 2025 U.S.–China Trade Deal?
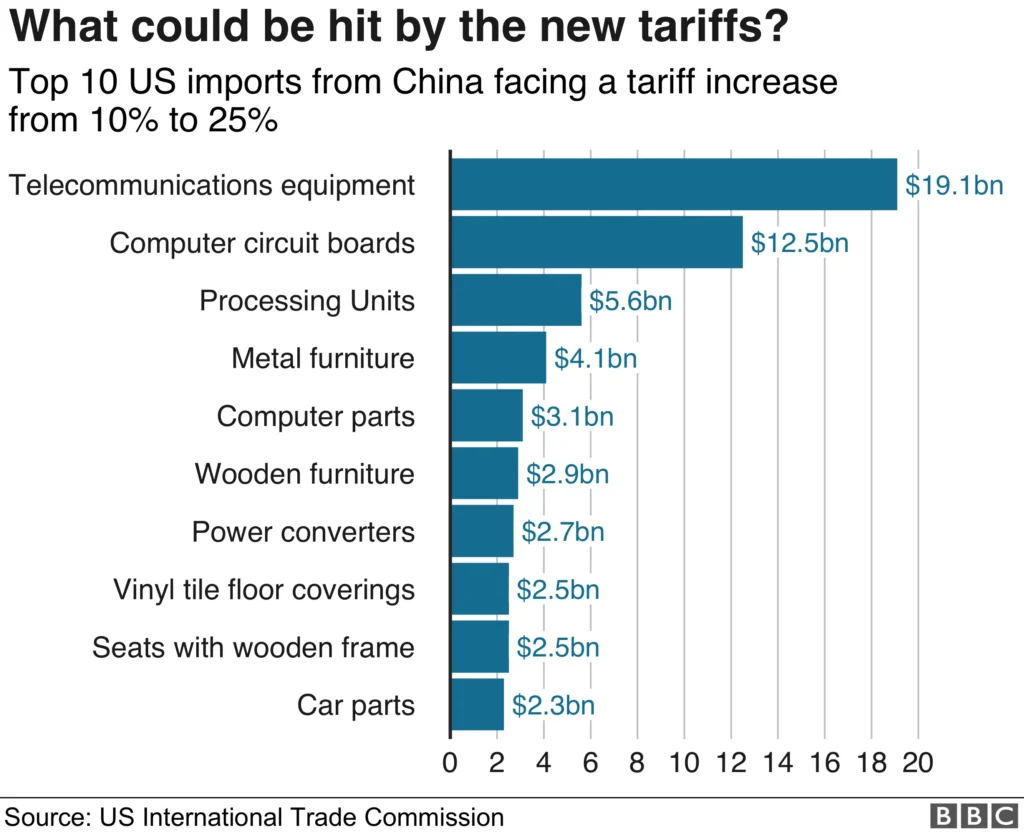
The latest trade deal between the U.S. and China was signed in Geneva in early May 2025. According to official reports, both nations agreed to reduce tariffs significantly over a 90-day period, with the U.S. cutting tariffs on Chinese goods from 145% to 30% and China reducing tariffs on American imports from 125% to 10%. This temporary truce in the ongoing trade war offers relief to businesses and consumers while opening the door for further negotiations.
The deal was brokered by high-level officials including U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer and China’s top economic advisor. Their goal was to create a win-win framework that would slow down the decoupling of the two largest economies and stabilize global markets.
Economic Relief for American Businesses
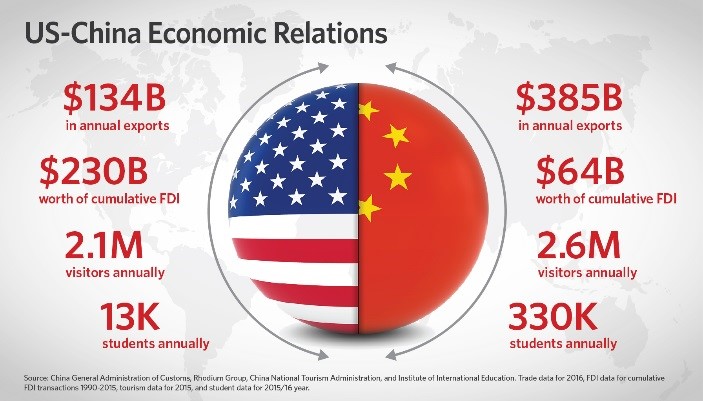
One of the primary goals of the agreement was to ease the pressure on American manufacturers and exporters. High tariffs imposed during the trade war had led to increased costs for companies reliant on Chinese raw materials and components. The rollback of tariffs will reduce these costs, potentially increasing profitability across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, and apparel.
Small businesses in the U.S. that rely on affordable Chinese imports are especially expected to benefit. The decrease in import costs allows these firms to reinvest savings into their operations, potentially leading to job creation and innovation. Major corporations such as Apple, Tesla, and General Electric have already seen market optimism reflected in their stock performance.
Impact on Consumers: Lower Prices and Greater Access
American consumers are among the biggest winners from the tariff reduction. Throughout the trade war, the cost of imported goods rose sharply, hitting consumer electronics, household products, and everyday essentials. With reduced tariffs, prices are expected to stabilize or even decline, putting more money back into consumers’ pockets.
Increased access to affordable goods from China also enhances consumer choice, while easing inflationary pressures that have plagued the post-pandemic economy. Retailers such as Walmart and Target anticipate lower wholesale prices, which could lead to more competitive pricing strategies.
Boost in Stock Market Confidence

The stock markets responded positively to news of the china trade deal. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), S&P 500, and Nasdaq all saw immediate gains following the announcement. Investors viewed the deal as a step toward reducing global uncertainty and boosting corporate earnings. Key stock futures indicators like Dow futures, S&P futures, and Nasdaq futures trended upward in the days following the agreement.
Sectors such as technology, finance, and manufacturing led the rally. Companies with heavy exposure to Chinese markets or supply chains experienced sharp rebounds, and investor sentiment shifted from risk-off to risk-on. The reduced volatility in futures markets suggests increased investor confidence in long-term economic growth.
Treasury Yields and Currency Movements
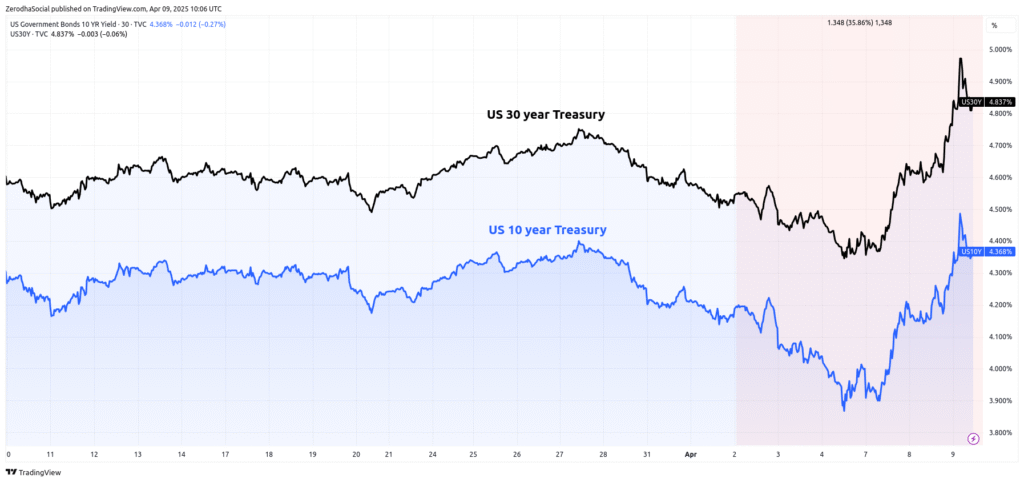
The agreement also influenced the bond and currency markets. As optimism grew, the yield on the 10-year Treasury rose, reflecting investor expectations for stronger economic growth. Higher yields typically indicate confidence in the economy and can also influence borrowing costs across the country.
Meanwhile, the U.S. dollar appreciated slightly against the Chinese yuan and other major currencies, signaling increased demand for dollar-denominated assets. This trend can have mixed effects, making U.S. exports slightly more expensive but attracting foreign investment.
Key Industry Impacts
Technology Sector: U.S. tech companies heavily dependent on Chinese manufacturing, such as Apple and Nvidia, stand to gain significantly from lower component costs and improved export conditions.
Agriculture: American farmers have long been impacted by retaliatory tariffs. With China reducing tariffs on U.S. agricultural goods, exports of soybeans, pork, and corn are expected to rise.
Retail and E-commerce: Lower tariffs mean reduced sourcing costs for large retailers, enhancing margins and potentially leading to discounts for consumers.
Energy and Resources: Companies exporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) and oil to China could benefit from improved trade relations and reduced regulatory friction.
Political and Diplomatic Implications
The deal also carries substantial political weight. For the U.S. government, it’s a demonstration of strong economic leadership and diplomatic strategy. For China, it presents an opportunity to stabilize its slowing economy. However, critics argue that the deal lacks enforcement mechanisms and fails to address deeper issues such as intellectual property theft and technology transfer.
Domestically, the deal may serve as a political win for the current U.S. administration, especially among moderate and business-friendly voters. However, labor unions and some advocacy groups have expressed concern over job outsourcing and continued dependence on Chinese manufacturing.
International Reaction and Switzerland’s Role
Switzerland hosted the final negotiations and played a neutral mediating role in the agreement. Global markets reacted positively, with stock exchanges in Europe and Asia also posting gains. Economies closely tied to U.S.–china trade deal, such as Germany, South Korea, and Japan, stand to benefit from the de-escalation.
International organizations like the WTO and IMF praised the deal as a sign that multilateralism still has a role in resolving trade disputes. However, many countries remain cautious, aware that future tensions could disrupt the fragile truce.
Ongoing Challenges and Unresolved Issues
Despite the optimism, several structural issues remain. The agreement is a temporary measure, and both sides have a long list of grievances:
- Intellectual Property Protections: U.S. companies continue to express concern about forced technology transfer and IP theft.
- Human Rights and Labor Issues: Broader geopolitical tensions still linger, including debates around human rights.
- Trade Imbalances: The U.S. trade deficit with China remains a political and economic concern.
- Enforcement: Critics worry about the lack of strong enforcement language in the current deal.
A Cautious Step Forward
The 2025 U.S.–China trade deal offers temporary relief and renewed hope for stronger economic collaboration between two superpowers. While businesses and markets have reacted positively, the deal is just one chapter in a long story of competition, cooperation, and complexity. If managed carefully, it could serve as a turning point that stabilizes global trade and encourages long-term investment.
As policymakers continue to navigate the intricacies of global commerce, the lessons from this deal will shape the future of international trade, economic growth, and geopolitical strategy.
Read more about Business and Latest News

