How Teleradiology Supports Rural and Underserved Healthcare Facilities
Introduction
Healthcare disparities between urban centers and rural or underserved areas are well-documented. These regions frequently struggle with limited access to medical specialists, including radiologists. According to the World Health Organization, rural areas are often characterized by fewer healthcare providers, longer travel distances to hospitals, and higher rates of chronic disease.
Radiology services are especially critical for diagnosing a wide range of conditions—from fractures and infections to cancer and cardiovascular disease. Without immediate access to radiological expertise, patient outcomes may be compromised due to delayed diagnoses and treatment. Teleradiology helps alleviate this burden by enabling the remote interpretation of diagnostic images, allowing rural facilities to offer a broader range of services without the need for on-site radiologists.
Definition
Teleradiology is the practice of transmitting medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, from one location to another for interpretation by a radiologist. This technology enables remote diagnosis and consultation, allowing healthcare providers to access expert opinions without requiring the radiologist to be physically present, thereby improving access to timely and specialized care, especially in rural or underserved areas.
How Teleradiology Works
Medical pictures like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds are digitally transmitted to radiologists who are stationed elsewhere in teleradiology. The images are typically captured at a local healthcare facility, uploaded securely via a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), and then transmitted over encrypted internet connections to off-site radiologists for analysis.
Once the radiologist reviews the images, a report is generated and sent back to the originating facility. This workflow can occur in real-time (synchronous) or be completed within a defined time frame (asynchronous), depending on the urgency and type of service required.
Key Benefits of Teleradiology for Rural and Underserved Communities
Improved Access to Specialist Care:
Teleradiology eliminates geographical barriers by connecting local healthcare providers with board-certified radiologists, regardless of location. This allows small clinics and rural hospitals to offer comprehensive diagnostic services that would otherwise be unavailable, ultimately ensuring patients receive high-quality care close to home.
Faster Diagnosis and Treatment:
In emergency situations, such as trauma or stroke, timely imaging and diagnosis are critical. Teleradiology enables rapid turnaround times by offering 24/7 access to radiologists who can provide immediate interpretations, especially during nights and weekends when on-site specialists may be unavailable.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Hiring full-time radiologists in low-volume rural facilities is often not financially viable. Teleradiology allows healthcare institutions to access diagnostic services on an as-needed basis, reducing overhead costs associated with full-time staffing while maintaining high standards of care.
Enhanced Clinical Collaboration:
By integrating teleradiology into their workflows, rural healthcare providers can engage in more robust clinical collaboration. Radiologists can consult directly with primary care providers and specialists, facilitating multidisciplinary approaches to complex medical cases and improving diagnostic accuracy.
Workforce Optimization:
Teleradiology helps address radiologist shortages by making efficient use of the existing workforce. Radiologists can interpret images from multiple facilities across different time zones, enabling better coverage and distribution of workload. This model also supports a more flexible work environment for radiologists, helping with retention and job satisfaction.
Applications of Teleradiology in Rural Healthcare
Teleradiology is utilized across various diagnostic and clinical scenarios in underserved areas:
- Emergency Services: Immediate interpretation of trauma-related imaging can guide life-saving interventions.
- Chronic Disease Management: Monitoring conditions like cancer, diabetes-related complications, and heart disease is made easier through consistent imaging access.
- Maternal and Child Health: Prenatal ultrasounds and pediatric imaging are available without requiring travel to distant urban centers.
- Second Opinions: Rural doctors can seek expert opinions to confirm or refine diagnoses, improving patient confidence and care outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, the implementation of teleradiology in rural settings comes with several challenges:
Infrastructure Limitations:
Reliable internet connectivity, sufficient bandwidth, and access to digital imaging equipment are essential for teleradiology. Many rural facilities may lack the technological infrastructure to fully support these services.
Data Security and Privacy:
The transmission of medical images and patient data must comply with strict data protection regulations such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. Ensuring end-to-end encryption, secure storage, and user authentication is vital to maintaining patient confidentiality.
Quality Assurance and Standardization:
To ensure diagnostic accuracy, teleradiology services must adhere to established clinical protocols, quality assurance practices, and standard reporting formats. Accreditation from relevant bodies, such as the American College of Radiology (ACR), helps maintain high standards.
Licensing and Regulatory Compliance:
Radiologists must be licensed to practice in the jurisdiction where the patient is located. This can complicate cross-border services and requires careful attention to regulatory frameworks, especially in international teleradiology operations.
The Future of Teleradiology in Rural Health
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and mobile health are expected to further revolutionize teleradiology. AI-powered tools can assist radiologists by prioritizing critical cases, identifying anomalies, and even generating preliminary reports – enhancing speed and accuracy.
Additionally, mobile teleradiology units and point-of-care imaging devices are becoming more accessible, allowing for portable and community-based diagnostic services. These innovations will likely expand the reach of radiological care to even more remote and marginalized populations.
Government initiatives and public-private partnerships are also playing a crucial role. Investment in rural broadband infrastructure, training programs for healthcare workers, and subsidized technology adoption can help overcome current barriers and promote widespread implementation of teleradiology.
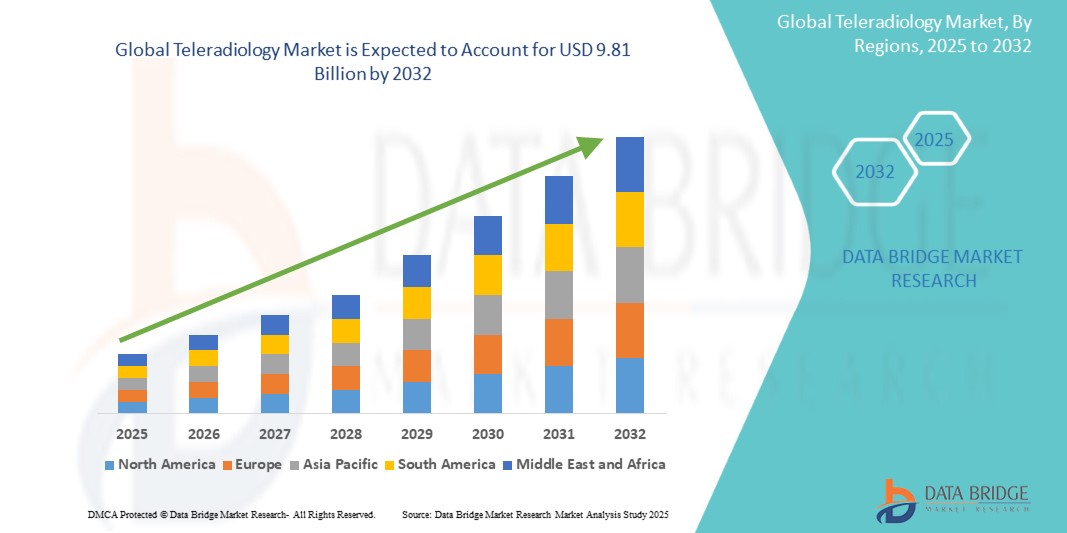
Growth Rate of Teleradiology Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the worldwide teleradiology market was predicted at USD 2.52 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.50% to reach USD 9.81 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-teleradiology-market
Conclusion
Rural and neglected healthcare is changing due to the potent instrument of teleradiology. By overcoming geographical and resource-related limitations, it provides critical diagnostic support, accelerates patient care, and strengthens health systems in areas that need it most.