What is the Best Medicine for Worms in Humans?
Intestinal worms, also known as parasitic worms, are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. These parasites enter the body through contaminated food, water, or poor hygiene practices and can cause a range of symptoms, including stomach pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss. While there are several medications available to treat worm infections, finding the best one for humans is essential for fast and effective relief.
In this comprehensive blog, we will explore the best medicine options for treating worms in humans, how these medications work, and what makes fenbendazole pills for humans a standout choice for some patients. We’ll also provide information on different treatment protocols and prevention tips to keep you and your family worm-free.
Understanding Worm Infections in Humans
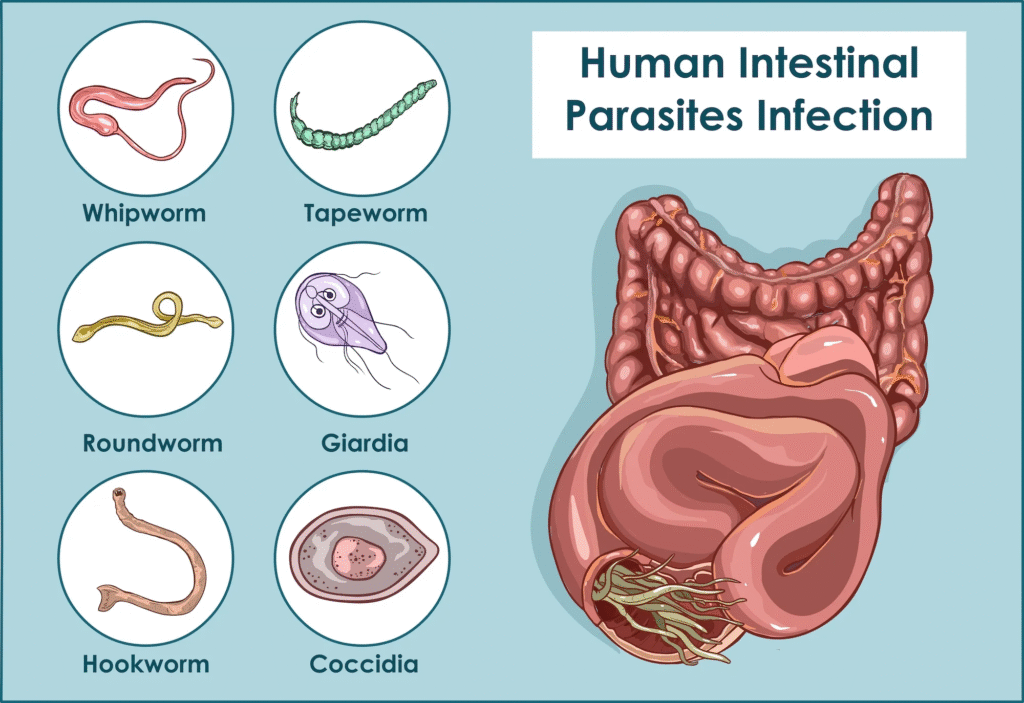
Before diving into treatment options, it’s important to understand what worm infections are. There are several types of parasitic worms that can infect humans:
- Roundworms (Ascaris)
- Hookworms
- Pinworms
- Tapeworms
- Whipworms
These worms can be transmitted through soil, food, water, or contact with infected individuals. Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of infection but may include:
- Abdominal discomfort
- Bloating
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Itchy anus (especially with pinworms)
In some cases, untreated worm infections can lead to malnutrition, developmental issues in children, and more severe health problems.
Common Anthelmintic Medications for Worms
Anthelmintics are drugs that expel parasitic worms from the body. Here are the most commonly prescribed medications:
1. Albendazole
Albendazole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic used to treat a variety of worm infections. It works by inhibiting the worm’s ability to absorb glucose, ultimately killing it.
2. Mebendazole
Mebendazole is often prescribed for treating pinworms, roundworms, and hookworms. It is well-tolerated and effective for single-dose treatment in many cases.
3. Ivermectin
This medication is particularly effective against strongyloidiasis and other parasitic infections, including lice and scabies.
4. Pyrantel Pamoate
Pyrantel is commonly available over the counter and is used primarily for treating pinworm infections in children and adults.
Introducing Fenbendazole: A Promising Alternative
Fenbendazole is a well-known antiparasitic medication used in veterinary medicine. Recently, it has gained attention for its potential use in humans under medical supervision. While originally developed for animals, some healthcare providers have started exploring fenbendazole pills for humans for their anthelmintic properties and even potential off-label applications in cancer management.
Fenbendazole works by interfering with the energy metabolism of parasitic worms. It binds to tubulin, preventing the formation of microtubules and inhibiting glucose uptake, ultimately starving the parasite.
The Role of Fenbendazole 500 mg in Human Treatment
Fenbendazole 500 mg is a commonly used dosage form when exploring human treatment options under expert guidance. This strength is considered potent and effective in clearing parasitic infections when used correctly. Some anecdotal and preliminary research data suggest that fenbendazole may also have broader biological impacts, although more scientific studies are needed to validate such claims.
It’s important to emphasize that the use of fenbendazole for human treatment should always be under professional medical supervision, especially considering dosage adjustments and potential side effects.
What is Wormentel 500?
Wormentel 500 is a branded formulation that contains fenbendazole as its active ingredient. It has recently emerged in discussions around alternative parasite treatments for humans. While it is not widely available in all pharmacies, online platforms such as Genericcures offer access to such medications at affordable prices for those who need them.
When considering Wormentel 500, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any treatment. Self-medicating without guidance can lead to complications or incomplete treatment.
How to Take Deworming Medication
Whether you are prescribed albendazole, mebendazole, or fenbendazole-based products, the administration is usually straightforward:
- Single Dose: Often sufficient for treating mild worm infections.
- Repeated Doses: In some cases, especially for tapeworms or persistent roundworms, multiple doses over several days may be required.
- With Food: Many of these medications are best taken with meals to enhance absorption.
- Follow-up: A second dose is sometimes recommended after 2 weeks to ensure all eggs and larvae are eliminated. And for more information, visit deworming tablets for adults.
Always follow the dosage and duration prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Safety and Side Effects
Most anthelmintic medications are well-tolerated. However, some side effects may include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Mild abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Temporary dizziness
Fenbendazole, in particular, is generally well-tolerated in humans in controlled doses, but long-term safety data is limited. Individuals with liver issues or those who are pregnant should consult their doctors before starting any new medication.
Natural Remedies: Do They Work?
While medications are the most reliable option, some people also explore natural remedies such as:
- Papaya seeds
- Garlic
- Pumpkin seeds
- Wormwood and black walnut extract
These remedies may help reduce symptoms, but they are not a substitute for proper medical treatment. Relying solely on natural methods may result in incomplete worm eradication and continued health issues.
Preventing Worm Infections

Prevention is key in avoiding recurring parasitic infections. Here are some essential prevention tips:
- Wash hands thoroughly after using the toilet and before eating
- Drink clean, filtered water
- Cook meat thoroughly to kill parasites
- Avoid walking barefoot in contaminated soil
- Deworm pets regularly and maintain hygiene
Public health initiatives in many countries now promote routine deworming in children and at-risk populations to reduce the global burden of these infections.
Conclusion: What is the Best Medicine for Worms?
The best medicine for worms in humans depends on the type of worm, severity of infection, and individual health status. Traditional treatments like albendazole and mebendazole remain highly effective, while newer alternatives such as fenbendazole 500 mg and Wormentel 500 are gaining attention for their promising results under medical guidance.
Whichever treatment you choose, make sure it’s backed by a healthcare professional’s recommendation. Timely intervention, proper hygiene, and periodic deworming can go a long way in ensuring a worm-free and healthier life.

